- 您现在的位置:买卖IC网 > Sheet目录1193 > AD-UCOS3-SPRD (Analog Devices Inc)PRD LIC UCOS3 RTOS CORE CCES SGL
�� �
�
 �
�Chapter� 5�
�5-1� ASSIGNING� TASK� PRIORITIES�
�Sometimes� task� priorities� are� both� obvious� and� intuitive.� For� example,� if� the� most� important�
�aspect� of� the� embedded� system� is� to� perform� some� type� of� control� and� it� is� known� that� the�
�control� algorithm� must� be� responsive� then� it� is� best� to� assign� the� control� task(s)� a� high�
�priority� while� display� and� operator� interface� tasks� are� assigned� low� priority.� However,� most�
�of� the� time,� assigning� task� priorities� is� not� so� cut� and� dry� because� of� the� complex� nature� of�
�real-time� systems.� In� most� systems,� not� all� tasks� are� considered� critical,� and� non-critical�
�tasks� should� obviously� be� given� low� priorities.�
�An� interesting� technique� called� rate� monotonic� scheduling� (RMS)� assigns� task� priorities�
�based� on� how� often� tasks� execute.� Simply� put,� tasks� with� the� highest� rate� of� execution� are�
�given� the� highest� priority.� However,� RMS� makes� a� number� of� assumptions,� including:�
�■�
�All� tasks� are� periodic� (they� occur� at� regular� intervals).�
�■�
�Tasks� do� not� synchronize� with� one� another,� share� resources,� or� exchange� data.�
�■�
�The� CPU� must� always� execute� the� highest� priority� task� that� is� ready� to� run.� In� other�
�words,� preemptive� scheduling� must� be� used.�
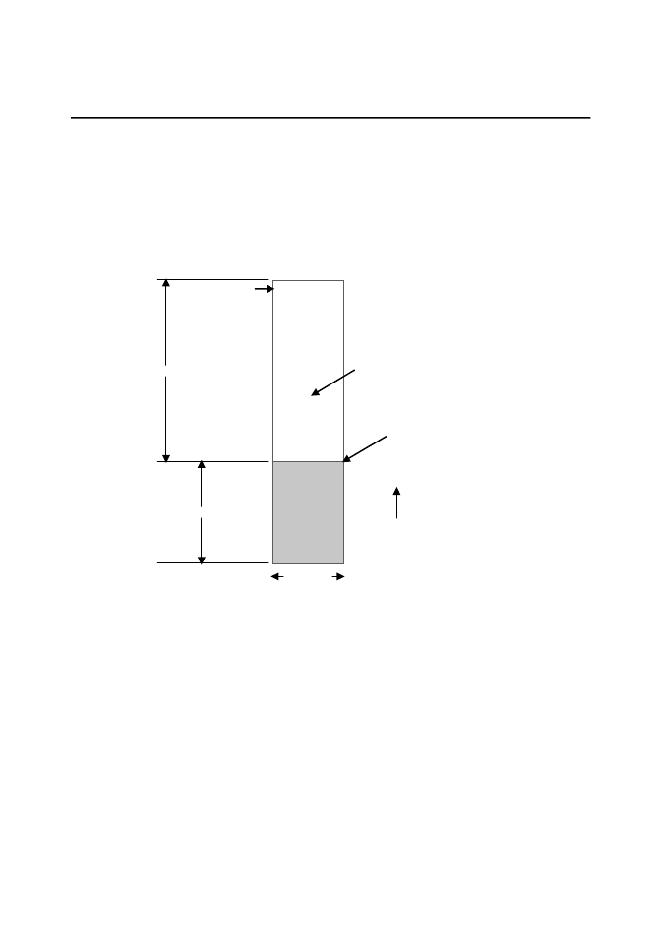
�Given� a� set� of� n� tasks� that� are� assigned� RMS� priorities,� the� basic� RMS� theorem� states� that� all�
�task� hard� real-time� deadlines� are� always� met� if� the� following� inequality� holds� true:�
�Where� Ei� corresponds� to� the� maximum� execution� time� of� task� i� ,� and� Ti� corresponds� to� the�
�execution� period� of� task� i� .� In� other� words,� Ei/Ti� corresponds� to� the� fraction� of� CPU� time�
�required� to� execute� task� i� .�
�Table� 5-1� shows� the� value� for� size� n(2� 1/n� –� 1)� based� on� the� number� of� tasks.� The� upper�
�bound� for� an� infinite� number� of� tasks� is� given� by� ln(2)� ,� or� 0.693� ,� which� means� that�
�meeting� all� hard� real-time� deadlines� based� on� RMS,� CPU� use� of� all� time-critical� tasks� should�
�be� less� than� 70� percent!�
�84�
�发布紧急采购,3分钟左右您将得到回复。
相关PDF资料
AD-UCUSBD-SPRD
PRD LIC UCUSB DEV CORE CCES SGL
AD637-EVALZ
BOARD EVALUATION FOR AD637
AD736-EVALZ
BOARD EVALUATION FOR AD736
AD737-EVALZ
BOARD EVALUATION FOR AD737
AD8007AKS-EBZ
BOARD EVAL FOR AD8007AKS
AD8018ARU-EVAL
BOARD EVAL FOR AD8018
AD8034ART-EBZ
BOARD EVAL FOR AD8034ART
AD8040AR-EBZ
BOARD EVAL FOR AD8040AR
相关代理商/技术参数
ADUCOSC100
制造商:Analog Devices 功能描述:ADC - Rail/Tube
ADUCOSC100-REEL
功能描述:DAC MICROCONVERTER DUAL TSSOP 制造商:analog devices inc. 系列:* 零件状态:上次购买时间 标准包装:1
ADUCOSC100-REEL7
功能描述:DAC MICROCONVERTER DUAL TSSOP 制造商:analog devices inc. 系列:* 零件状态:上次购买时间 标准包装:1
ADUCOSCZ100
制造商:Analog Devices 功能描述:
ADUCOSCZ100-REEL7
制造商:Analog Devices 功能描述:ANAADUCOSCZ100-REEL7 12 BIT ADC WITH EMB
ADuC-P7026
功能描述:开发板和工具包 - ARM PROTOTYPE BRD FOR ADUC7026 ARM7 RoHS:否 制造商:Arduino 产品:Development Boards 工具用于评估:ATSAM3X8EA-AU 核心:ARM Cortex M3 接口类型:DAC, ICSP, JTAG, UART, USB 工作电源电压:3.3 V
ADUCRF101
制造商:Analog Devices 功能描述:PRECISION ANALOG MICRCONTROLLER - Tape and Reel
ADUCRF101BCPZ128
制造商:Analog Devices 功能描述:PRECISION ANALOG MICROCONTROLLER WITH RF TRANSCEIVER, ARM CO - Trays